Hot Rods
When it comes to performance, the devil really is in the details. Ever wonder why one engine makes more power than another, when both are seemingly identical? The answer to this very common performance question lies in the attention to detail. Basic performance elements such as engine tuning, spark timing curves, and, yes, even oil selection all come into play when you attempt to extract the maximum amount of power from your existing combination.
Time and time again, our advice to those interested in learning about stout-running engines is that it’s the total combination that makes it all happen—considering, of course, that components are prepped, cleaned and assembled as if in a “clean room.”
There are many reasons why the icon cars have achieved the lofty status they now enjoy, but one of the more obvious reasons is the simple fact that they were finished. Their existence and subsequent high-level exposure have inspired many a young lad to undertake similar projects, and for every famous car built in the early years, probably two others were started in an attempt to either copy or outdo it, but they never saw the light of day.
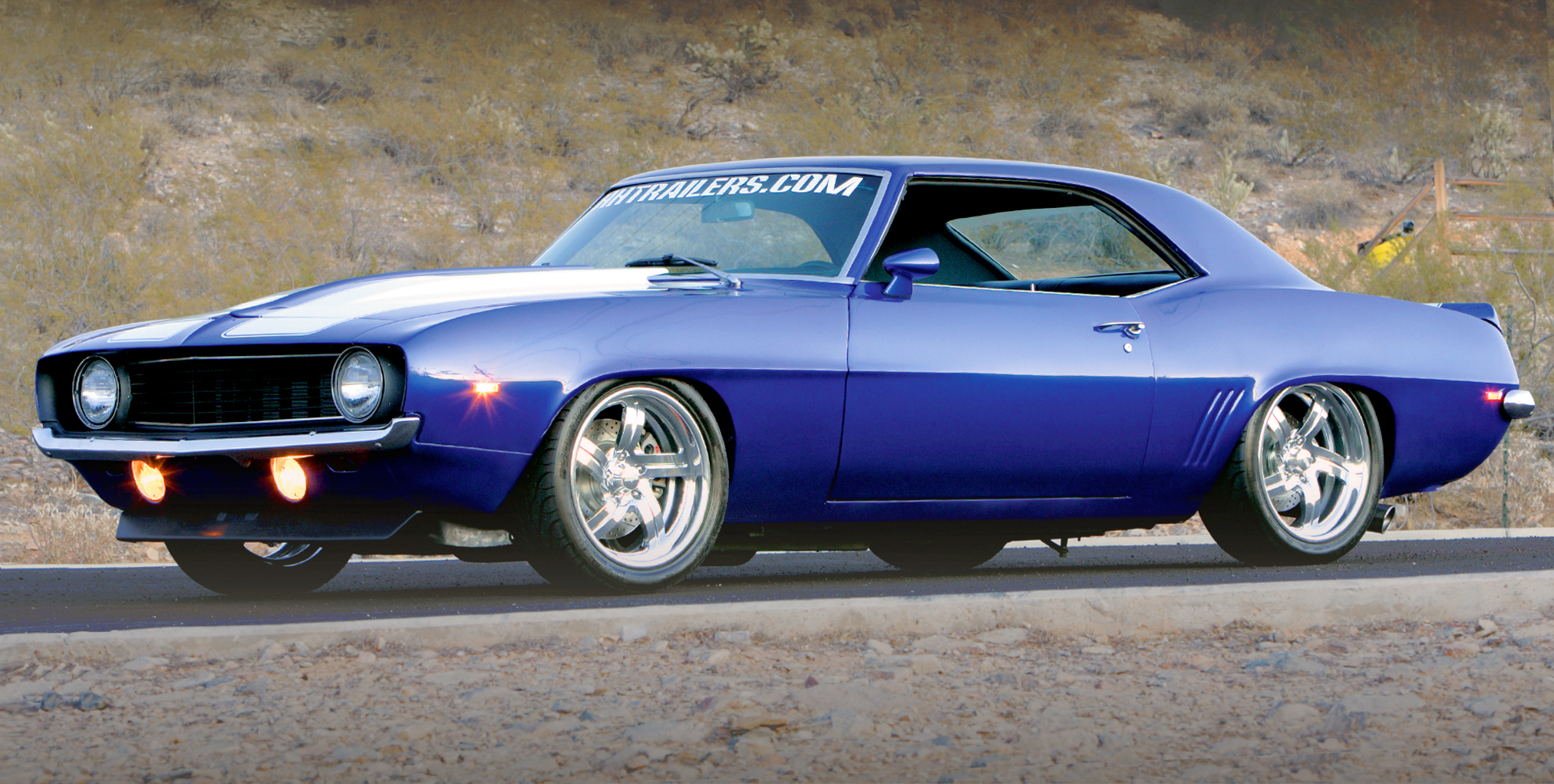

The late ’60s was a good time for automobile enthusiasts everywhere. For Chevrolet specifically, it remains a time when the company produced vehicles that are among the favorites of Bow Tie aficionados. Who wouldn’t want a ’67-’69 Chevy Chevelle, Nova or, of course, the ever-popular Camaro? The design of these vehicles, and many others from that era, has stood the test of time, and car manufacturers today are even reverting back to the styling cues of these classics when designing modern production cars.
Have you ever noticed how some people can take their car to the strip and look as if they’ve raced all their lives, while others look totally out of control in the bleach box and during staging? More often than not, the driver with the calm, cool and collected approach seems to regularly trigger the win light. The reason for this smoothness isn’t completely initiated by the driver; in most instances, it is the correlation between man and machine.
There’s no denying the popularity of Camaros; they have been a rodding favorite since their initial release in 1967. The first-generation Camaro has always been an enthusiast car because it is small, lightweight and had a sports-car-design feel to it. Underneath, the early Camaros were based on a Nova platform and featured many good mechanical attributes. Right from the start, they became a popular choice for teenagers and young adults, and most of the performance enthusiasts wanted the SS model that came with a choice of a strong-running small- or big-block engine. Things haven’t changed much, because they are still a popular choice for enthusiasts to restore or modify.
We first wrote about this 565-cubic-inch Dart “Big M” engine, equipped with Dart Big Chief II Pro Stock-type aluminum heads, back in our October ’04 issue. The engine builder was Quarter Mile Performance in Chatsworth, California, and at the time, we called it “possibly the world’s most powerful four-barrel big-block.” It produced 1037 horsepower at 7200 rpm and 806 lb-ft of torque at 5500 rpm–plenty stout by anyone’s standards.
The small-block Chevy has enjoyed a long, happy life. Sure, the current LS1/LS6 version is quite far removed from the original, but thousands upon thousands of little mouse motors continue to provide the sole means of motivation to everything from stationary irrigation pumps to Le Mans-winning C5R Corvettes. Naturally, this list also includes all manner of boulevard bruisers, street stompers and resto rockets. Heck, we’ve even seen little Chevys under the hood of “Brand X” machinery. The continued popularity of the small-block Chevy is not surprising. Take a look at the combination of power potential and parts availability and multiply that by the cost quotient, and you have the makings of a real success story. Add to this equation the millions of project motors just sitting around junkyards throughout the world, and it is easy to see why enthusiasts continue to embrace the mighty mouse motor as the performance powerplant of choice.